Unleashing Your Startup's Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to Building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
- July 17, 2023
- Posted by: mapannoir
- Category: News
Introduction
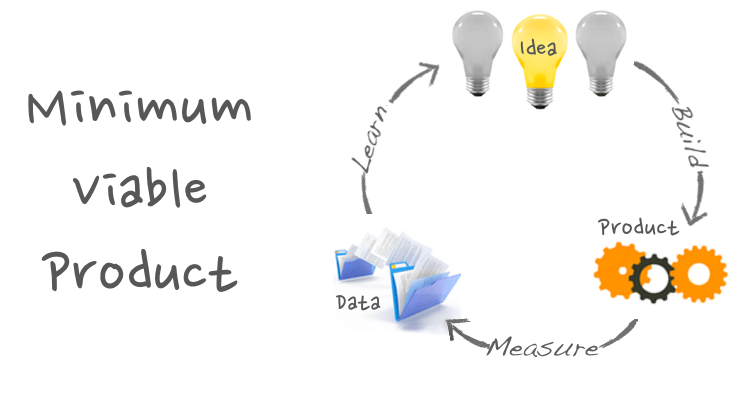
Launching a startup is an exhilarating endeavor, but it can also be daunting. One of the most critical early steps in this journey is building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP). An MVP is a foundational version of your product that includes just enough features to satisfy early adopters and gather valuable feedback for future iterations. In this guide, we will explore why an MVP is essential for startups, how to identify core features, build a scalable MVP, test and iterate based on customer feedback, and finally, when to launch your MVP and secure your initial customers.
1. The Importance of an MVP for Startups
An MVP holds immense significance for startups due to several key reasons:
- Market Validation: Building an MVP allows you to validate your startup idea with real customers and determine if there’s a market need for your product.
- Resource Optimization: By focusing on essential features, an MVP enables efficient allocation of resources, reducing time and costs.
- Rapid Learning: Early user feedback from the MVP empowers you to identify potential improvements and necessary changes quickly.
- Competitive Advantage: Being first to market with an MVP gives you a competitive edge, allowing you to fine-tune your product based on customer insights.
2. Identifying Core Features and Functionality
To build an impactful MVP, it’s crucial to identify the core features and functionality that will address your target users’ primary pain points. Consider the following steps:
- Market Research: Conduct in-depth market research to understand your target audience, their needs, and pain points.
- User Personas: Create detailed user personas to identify the specific problems your MVP must solve.
- Feature Prioritization: Prioritize features based on their importance, relevance, and potential to deliver value to early adopters.
- Lean Approach: Adopt a lean methodology, focusing on the most critical features that align with your startup’s vision.
3. Building a Scalable MVP
While an MVP is designed to be minimal, it should also be scalable to accommodate future growth. Follow these steps to ensure scalability:
- Flexible Architecture: Build a modular and flexible architecture that allows for easy integration of additional features in the future.
- Quality Code: Ensure your MVP is built with clean, maintainable code, reducing technical debt as you scale.
- Cloud Infrastructure: Consider using cloud-based infrastructure, which provides the scalability and flexibility required for future expansion.
- Data Management: Implement scalable data management practices, as data volumes will likely grow as your startup gains traction.
4. Testing and Iterating Your MVP Based on Customer Feedback
An MVP’s true value lies in its ability to gather user feedback and iterate accordingly. Follow these steps for effective testing and iteration:
- Early Adopter Outreach: Target early adopters and gather their feedback through surveys, interviews, and user testing.
- Feedback Analysis: Analyze the feedback collected from users to identify trends, pain points, and areas for improvement.
- Prioritized Iteration: Prioritize changes based on user feedback and focus on adding features that align with user needs.
- Continuous Learning: Embrace a culture of continuous learning and improvement, using data-driven insights to refine your MVP.
5. Launching Your MVP and Securing Initial Customers
Knowing when to launch your MVP and how to acquire initial customers is crucial for gaining momentum and attracting early adopters. Consider the following steps:
- Beta Testing: Conduct beta testing with a selected group of users to iron out any last-minute issues.
- Early Access Marketing: Use early access marketing to generate buzz and attract potential customers before your official launch.
- Customer Onboarding: Offer personalized onboarding experiences to new customers to ensure a positive initial experience.
- Referral Programs: Implement referral programs to encourage satisfied customers to spread the word about your MVP.
Conclusion
Building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a foundational step in launching a successful startup. By identifying core features, building a scalable MVP, testing and iterating based on customer feedback, and strategically launching to secure initial customers, you set your startup on a path to sustainable growth. Embrace the agile mindset of continuous improvement, and let your MVP evolve as you learn from your users. With a well-crafted MVP, you can confidently embark on your startup journey and realize your vision for success.
